Dry Stacked Block Construction Roof Design
Roof Types
There are only three primary roof designs. They consist of a HIP roof , a GABLED roof, and a flat roof. The hip roof has no gabled ends and more tie-down connection points for better wind survival. In a rectangular house the hip roof has four sections with each section sloping down from the roof peak down to the top of each house wall. See our book and the diagram below.
A rectangular house gabled roof has two roof sections sloping down from the roof peak towards two of the opposing house walls. The other two house walls continue up to the roof peak. These gabled walls present a large wind catch during severe wind conditions.
A flat roof lends itself to concrete roof material (no trusses) because it simplifies the pouring and screed of the concrete. Creation of the elevated forms to support the wet concrete until it cures is always an issue. Another problem is getting the cement from the mixer truck up onto the roof. A flat roof can also be sloping or pitched somewhat like a gabled roof. Typically the pitch is small resulting in a gentle slope that facilitates pouring and screed of the concrete. This slight pitch also expedites drainage of rain water. We have are created a separate web page on this concrete roof topic.
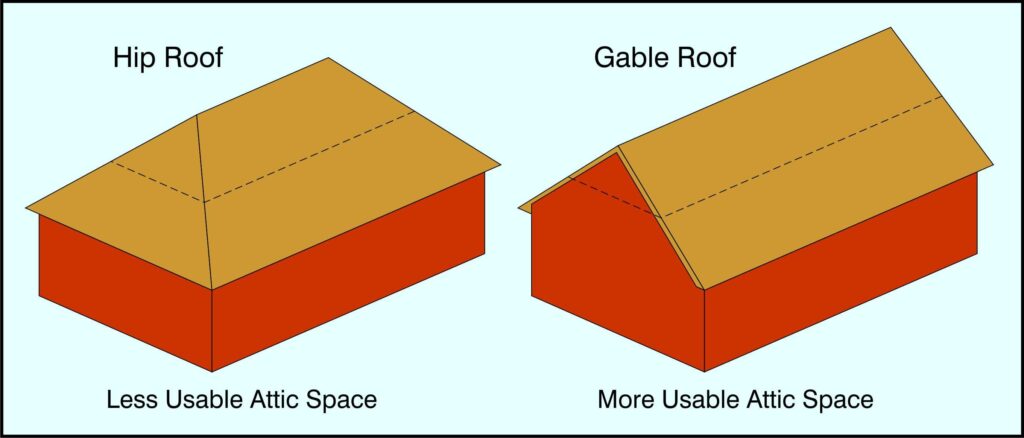
Ok, back to truss roof designs. The hip roof may be slightly more complex, but it doesn’t typically have any valleys which are prone to leaks. The gabled roof is less complex but it has two disadvantages. First it presents a wind catch for severe winds and secondly it takes more effort to make the lintel bond beam follow the gabled wall angles. This is achievable but it is extra effort to finalize a wind catch wall.
Trusses
Builders in today’s world specify trusses as the basis for the roof design. These engineered trusses are designed to fit your house plan. These trusses are designed to support the local maximum wind speed and snow loading requirements. These truss designs can also include a loft for your tiny house design.
Trusses will be used with dry stacked concrete block construction, unless a concrete roof is practical for your location. The empirical design building code allows simplistic non-engineered dry stacked block construction house plans when used with engineered trusses.
Soffits
Soffits are defined as the roof overhang where the roof meets the wall. Wide soffits reduce cooling costs by reducing the amount of sunlight that shines on the walls. Wide soffits reduce the sun heating of the walls in winter time. So your location will determine your soffit width.
Soffits will also impact wind catch during severe weather, and the soffit over-hang is factored into the truss design. In this consideration, narrow soffits are preferred for high wind areas and predominately cold climates. Wide soffits are incorporated for predominately warm climates where keeping the sun off the walls is important. Always consider you location before deciding on roof style and soffit width.
