Tiny/Small House with Dry Stacked Block
Typical rectangular tiny/small house floor plan
Ensuring extreme storm safety in a wooden stick-built tiny house presents challenges. However, a dry stacked concrete block tiny house eliminates these storm safety vulnerabilities. Your tiny home must provide unwavering safety, especially during severe weather. Our comprehensive book enables you with all the essential information to initiate and successfully complete your tiny house project.
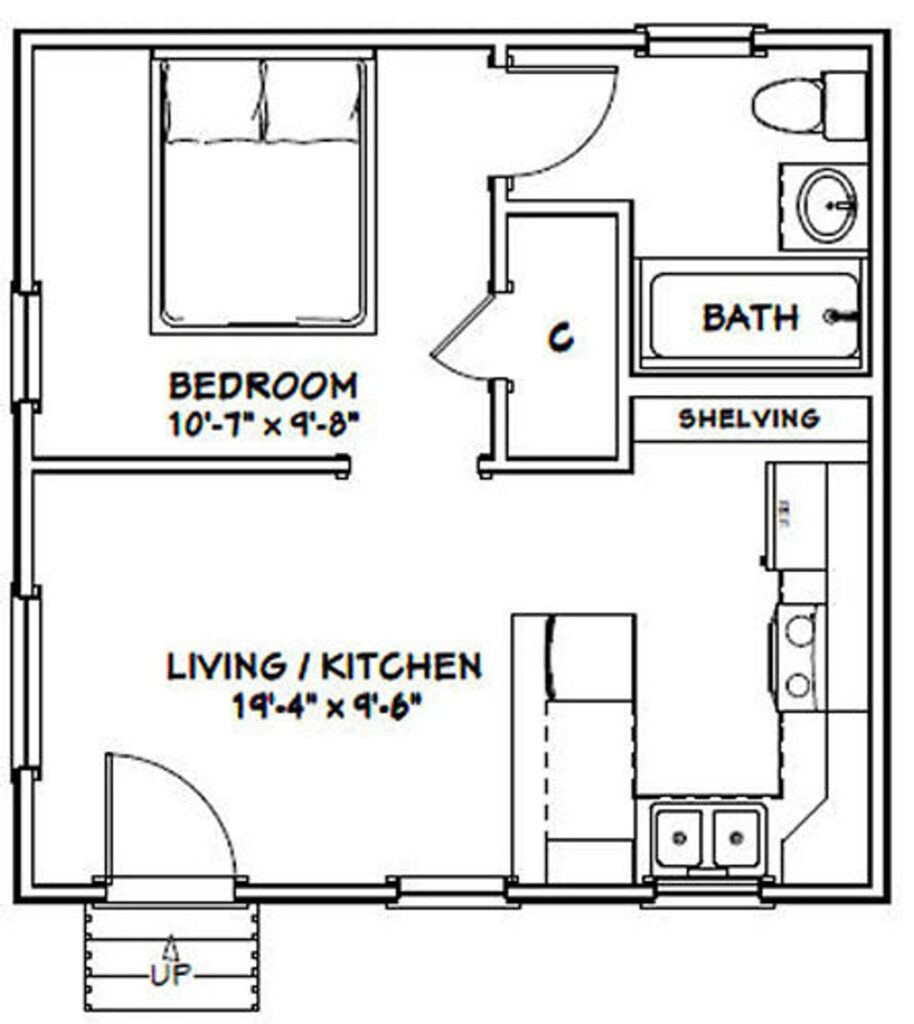
Above, you’ll find a typical rectangular floor plan for a tiny house, as showcased on https://www.pinterest.com. Opting for this design offers numerous advantages over a circular plan. If you’re seeking a non-circular, exceptionally wind-resistant, and durable structure that withstands the test of time, then a dry stacked concrete block tiny house is your ideal choice.
Insurance companies have introduced the concept of “fortified home standards,” which are increasingly becoming prerequisites for home insurance coverage. If you’re embarking on new home construction, closely heed this standard as it can significantly impact your homeowner insurance premiums and possibly leave you uninsured!
Typical tie down straps
The effectiveness of the tie-down anchoring system becomes crucial for portable tiny homes due to their low structural mass. In contrast, a dry stacked block tiny house gains its stability from its substantial mass, firmly connecting it to the ground. This inherent weight provides significant resistance against severe storms and extreme winds.
Furthermore, the structural design of a tiny house significantly influences its ability to withstand storms. The type of roof you choose plays a pivotal role in determining how well your home can weather severe conditions. Even if your home is securely anchored, a roof that gets torn off will result in catastrophic losses. This emphasizes the critical importance of proper roof attachment in designs meant to withstand high winds.
In scenarios with the potential for strong winds, like those experienced during a hurricane or nearby tornado, the inclusion of hurricane straps becomes indispensable. Traditional wooden stick-built homes necessitate an extensive application of strapping along the full height of the walls to enhance stability by creating a virtual connection with the structural foundation.
Enhanced tie down straps
In contrast, a dry stacked block home, equipped with a perimeter bond beam consisting of reinforced concrete and steel rebar encircling the top of the walls, establishes a robust connection for the roof. This arrangement culminates in the creation of short yet exceptionally secure concrete-embedded tie-down straps, effectively fastening the house roof to the ground.
The firm attachment to the earth is a direct outcome of the bond beam being firmly linked to the foundation of the structure. This connection is facilitated by vertically aligned wall cells, filled with concrete and rebar, spaced no more than 8 feet apart. These 8-foot wall cells are in addition to similar cells found at each corner, around windows, and surrounding door openings. The rebar-filled cells are integrated with the rebar from the foundation, resulting in a seamless connection between the entire perimeter of the bond beam and the foundation. As a result, these tie-down straps are now deeply embedded into the foundational structure of the building, eliminating any reliance on weak wooden attachment points.
Advantages of a dry stacked block tiny/small house
- Doesn’t have to be round to survive extreme weather
- Our how-to book is available for immediate download
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly: Tiny homes make it easier to minimize your carbon footprint that could help the environment in many ways—designed and built to give you precisely the amount of space you need, unlike traditional homes, which usually have unnecessary space
- Affordability: Tiny homes are often less expensive than traditional homes
- Energy Efficient: Tiny home reduced size requires less energy to heat and cool
- Additional 10% utility savings due to thermal mass of a concrete block house
- Surface bonding cement on block structures looks like trendy stucco
- No unhealthy formaldehyde laden building materials
- Strong structural mass is resistant to storm damage and high winds
- Earthquake resistant due to low cost rebar in footer, doorway openings, window openings, wall corners and the house perimeter, which also assures solid roof attachment
- Low carbon foot print because blocks are water-cured and do not require the burning of fossil fuels during manufacture
- Build in locations where wood structures would rot and eventually fail
- Safe against termites
- Draft-free and critter entry proof
- Lower construction costs
- Stacked blocks reduce use of costly cement
- Weather-resistant during extended construction delays
- Easy to stack and build by one or two people without any difficult skills (I stacked my entire house 7-rows high within 3-days by myself, it goes quite quickly)
- Small footprint on the property
Will your wood structure tiny/small house be safe?
The below round tiny house design increases the survive-ability of a wood stick house structure during extreme wind conditions. Building a round house is very challenging and also very unusual to live in. For example, sound from adjacent rooms can be quite annoying. Some owners may prefer being different (or exotic), but resale value may be diminished for those home buyers who think it is cute but not a desired lifestyle.
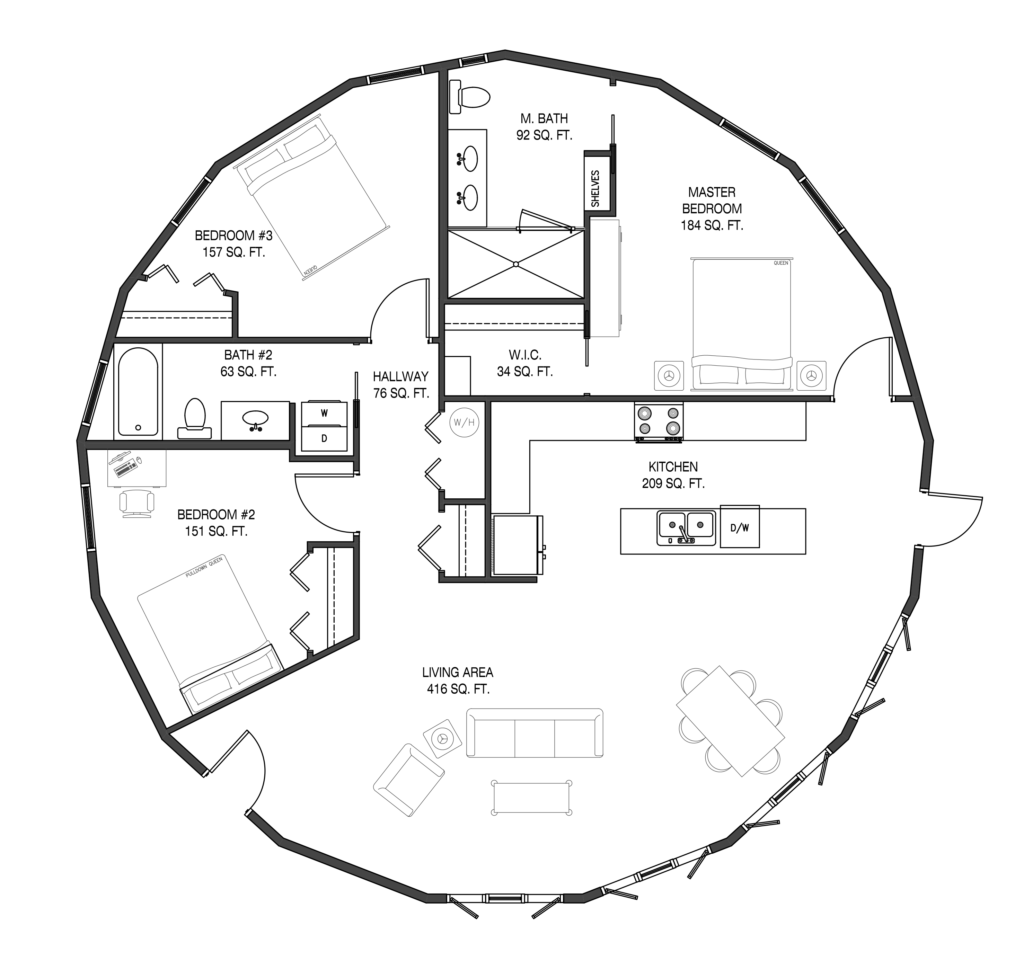
Shown above is a typical wood construction circular floor plan image found at https://www.pinterest.com. Construction of this wood stick design has many disadvantages over rectangular design:
- Non-conventional construction methods are used
- Interior design and build is complicated and costly
- Strength against severe weather and high winds diminishes with time
- Smaller selection of available floor plans
- Requires custom counter tops and custom floor covering installation
- Window and door framing is weak compared to dry stacked block construction
- Requires non-conventional roof design
- Roof tie-down points are weaker than in dry stacked block design
Final Design Thoughts
The decision to opt for a portable tiny house is accompanied by a significant consideration; the inherent uncertainty regarding the structural strength of such a dwelling. This is one of the trade-offs that requires your careful evaluation. Additionally, the choice for a portable tiny house introduces notable limitations on the possible shapes and dimensions for your living space.
Conventional gable roof designs have the propensity to catch the wind, potentially leading to damage when facing storms and strong wind gusts. In contrast, the design of a dry stacked block construction home typically employs the hip roof (or bonnet roof) style. This roofing design is particularly advantageous as it eliminates wind-catching concerns by removing gable ends and any roof sections that protrude. Each side of the hip roof commences at the wall’s height, a configuration that notably mitigates wind-catching tendencies, especially in the face of severe storms.
Trailer park devastation
The destruction witnessed in trailer parks during severe weather events is a stark reminder of the vulnerability that portable tiny houses share. While some may argue that a mobile tiny house is secure due to its ground strapping, it’s important to consider that those trailers in trailer parks were also ground strapped according to local code regulations. Yet, the effectiveness of this anchoring method and wood structure build is questionable considering the extent of damage incurred at these trailer parks.
Feeling safe and secure in your dry stacked block construction tiny house becomes paramount when facing extreme weather conditions. The degree of protection you have is intricately tied to the structural integrity of all components of the house and how they interconnect. Surface bonding cement (SBC) as well as rebar reinforced wall cells, plays a pivotal role in creating a cohesive structure by firmly uniting all wall components with the foundation. In contrast, relying solely on nails driven into wooden boards does not offer the same level of strength or safeguarding for your family.
